AMD: More detailed information about AMD processors can be found on their product page.
Here is additional information about AMD Ryzen 3, Ryzen 5, Ryzen 7, and Ryzen 9 processors:
AMD Ryzen 3
- Usage: Basic performance, suitable for light tasks such as browsing the internet, streaming videos, and using office applications.
- Number of Cores: Usually 4 cores.
- Clock Speed: Lower than Ryzen 5, 7, and 9 processors.
- Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT): Available in most models, allowing multiple threads to be executed simultaneously.
AMD Ryzen 5
- Usage: Mid-range performance, suitable for multitasking, light gaming, and content creation.
- Number of Cores: Usually 6 cores.
- Clock Speed: Higher than Ryzen 3 processors, and most models have Precision Boost feature to increase clock speed when needed.
- Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT): Available in all models, enhancing multitasking capabilities.
AMD Ryzen 7
- Usage: High performance needs, suitable for heavy multitasking, gaming, and demanding content creation.
- Number of Cores: Usually 8 cores.
- Clock Speed: Higher than Ryzen 5 processors, and Precision Boost feature is common.
- Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT): Available in all models, allowing multiple threads to be executed simultaneously.
AMD Ryzen 9
- Usage: Top-tier performance, suitable for very demanding tasks such as professional video editing, 3D modeling, and gaming.
- Number of Cores: Usually 12-16 cores.
- Clock Speed: Highest among Ryzen series processors, and Precision Boost feature is standard.
- Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT): Available in all models, maximizing multitasking capabilities.
Summary
- Ryzen 3: For basic use.
- Ryzen 5: Versatile and balanced performance.
- Ryzen 7: For high performance needs.
- Ryzen 9: Top-tier performance for demanding tasks.
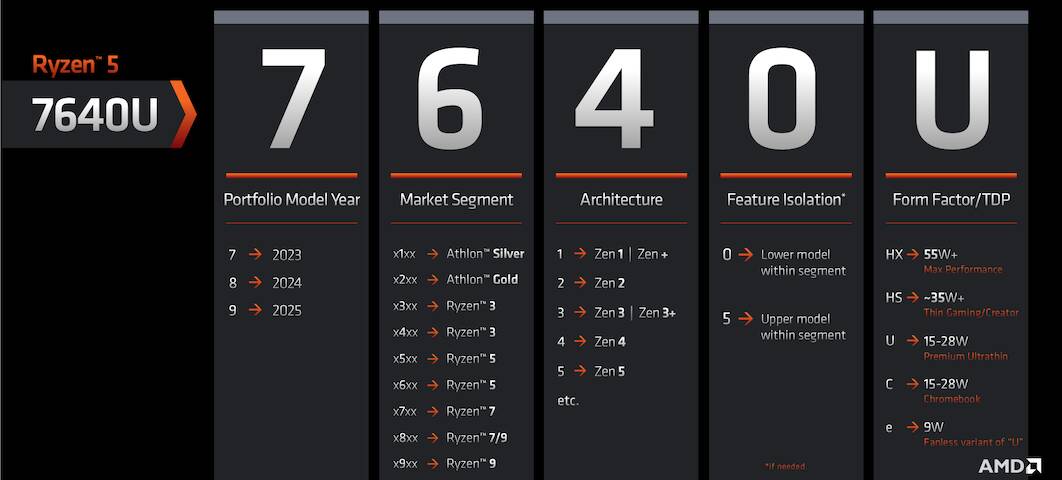
AMD Processor Model Numbers (Example)
AMD uses model numbers that typically consist of the following parts:
- Brand: For example, Ryzen.
- Model year: Digits like 7, 8, and 9 refer to 2023, 2024, and 2025, respectively.
- Market segment: The family of the processor, for example 5 and 6 are classified as Ryzen 5.
- Architecture: The microarchitecture of the processor (Zen 3, Zen 4, etc.)
- Feature Isolation: Model variant within the segment (0 is a lower model and 5 is an upper model)
- Suffix Letters: Letters such as X, G indicate additional features or the form factor/TDP:
E (9W): Ultra-low power chips used in budget laptops, typically fanless for quiet and cool operation.
C (15–28W): Power-efficient processors made specifically for Chromebooks.
U (15–28W): Designed for slim and lightweight laptops, balancing performance with long battery life.
HS (35W+): High-performance processors with built-in graphics, offering strong performance without using too much power.
HX (55W+): AMD’s top-tier mobile processors, built for maximum speed and power—ideal for gaming or demanding tasks.
3D: Stands for 3D V-Cache — a special technology that adds extra cache memory stacked vertically on the CPU. For example HX3D.
Example: AMD Ryzen 5 7540U
| Component | Meaning |
|---|
| Ryzen 5 | Segment (e.g., Ryzen 3, 5, 7, 9 – still indicates performance tier) |
| 7 | Model Year (7 = 2023) |
| 5 | Family within the segment (5 and 6 = Ryzen 5) |
| 4 | Microarchitecture (4 = Zen 4, a modern 5nm design) |
| 0 | Model variant (0 = base, 5 = higher-end within the family) |
| U | Power class (U = ultra-low power, suitable for thin/light laptops) |
Sometimes a lower number might actually mean a better processor, for example:
| Model Example | Architecture | Performance Class | Power Class |
|---|
| Ryzen 5 7540U | Zen 4 | Mid-range | Low power |
| Ryzen 7 7735U | Zen 3 | Upper mid-range | Low power |
When choosing a laptop with an AMD processor, don’t rely solely on the Ryzen 3/5/7/9 labels or assume that a higher number always means better performance.
The third digit in the model number is the most important, as it indicates the CPU architecture generation (e.g., 4 = Zen 4, newer and more efficient).
Also, pay attention to the suffix:
For example, although Ryzen 7 7735U may seem better than Ryzen 5 7540U, the latter is based on a newer architecture (Zen 4 vs. Zen 3) and actually delivers better performance in many cases.

